By Stephen Glaude – Vice President, Engineering
Solenoid valves have been used for more than 100 years in many diverse flow control applications, across many industries. But misunderstanding the underlying physics of their operation can lead to misapplication or suboptimal performance.
Exciting a simple solenoid coil with AC rather than DC power, for example, can provide higher forces in opening a poppet valve and thus may help counter higher differential pressures of the fluid at start up, but DC power may provide other advantages, such as ease of wiring and reduced shock hazard. Heat build-up is another issue that has hampered effective, energy-efficient solenoid operation.
This paper covers the basic operation of solenoid valves, including useful techniques and technology for optimizing performance, power consumption, and cost of operation, in either AC or DC powered applications.
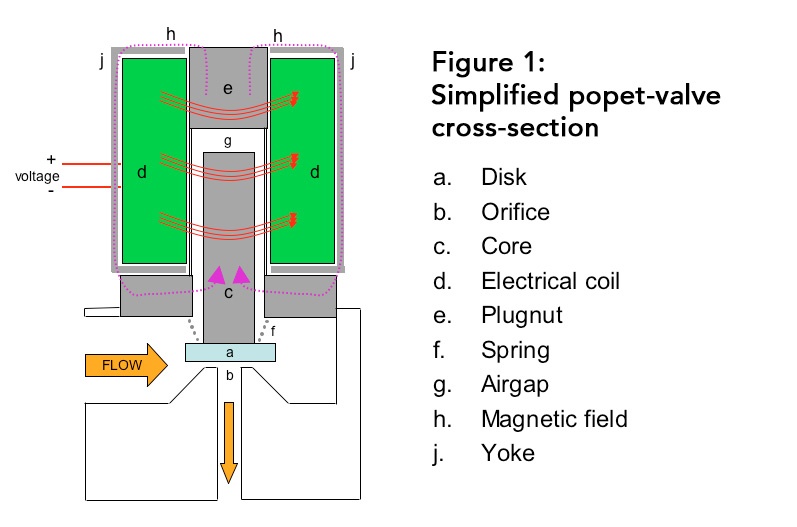
Figure 1 shows a simplified normally-closed poppet valve, depicting the disk (a), orifice (b), movable core (c), electrical coil (d), plugnut (e), conical spring (f), airgap (g), magnetic field (h), and yoke (j). When the surrounding electrical coil is not energized, there is, of course, no electromagnetic field and thus no electrical force pulling on the movable core. The disk attached to the core remains pressed against the orifice, stopping flow. The conical spring holds it in place there, until the coil is energized. The disk is typically made from an elastomeric material, which ensures a tight closure.
Passing electric current through the coil induces a magnetic field in the magnetically permeable circuit, comprised of the movable core and the stationary plugnut and yoke. The resulting electromagnetic force moves the core towards the plugnut, closing the airgap. This action compresses the conical spring, moving the disk from the orifice, allowing flow to commence. The larger the specified orifice, the greater flow coefficient (or Cv) — the amount of flow for a given pressure drop.
The simplified explanation above works equally well for AC or DC excitation, subtleties of internal construction notwithstanding. But analysis of performance at various stages of operation reveals differences that can be exploited to gain performance improvement and energy efficiencies.
When the valve is just starting to open, force from the spring helps keep the orifice covered, but this is augmented by hydraulic force produced by the pressure drop between the valve inlet and outlet. This hydraulic force is proportional to the square of orifice size, since the area of pressure imbalance is equal to pi times the orifice radius squared. This is why opening valves with greater flow often requires a disproportionately larger coil and lifting force.
However, once the valve is open and flow commences, the hydraulic force decreases dramatically. So an ideal solenoid valve should have just enough initial electromagnetic lifting force to counter both the spring tension and the hydraulic forces. But once flow starts and hydraulic force has diminished, the valve needs to consume only enough energy to compress the spring. Providing the same amount of energy required to counter the initial hydraulic force simply creates waste heat.
To manage solenoid power consumption across various states of operation, AC excitation is usually more efficient than DC. Typically, an end user will supply AC voltage to the coil by activating a mechanical or solid-state switch, for example. But the magnetic field is generated not by the voltage but by the current passing though the coil, multiplied by the number of coil turns. This current is equal to the voltage divided by the coil impedance.
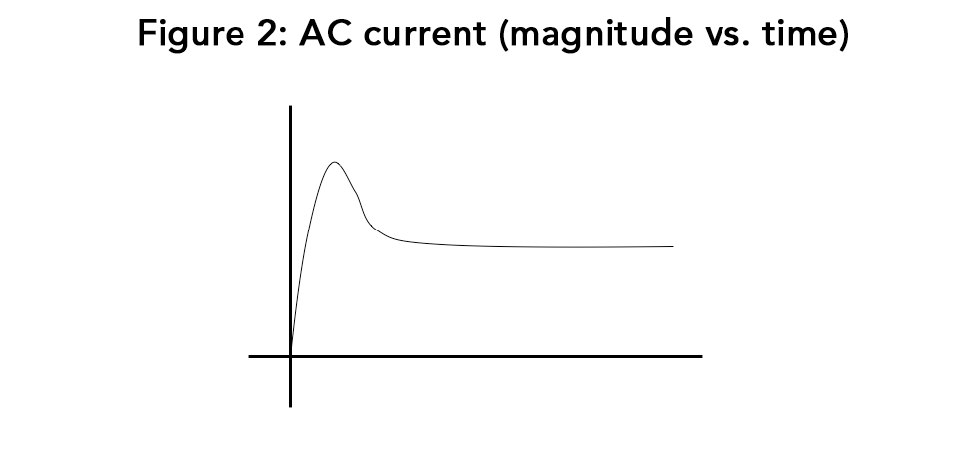
For an AC sine wave impedance is calculated as R + j*2*pi*f*L, where R is the coil resistance, L is its inductance, f is the AC frequency, and j is a mathematical operator that results in a 90-degree phase shift. As the solenoid valve opens, the air gap quickly narrows. The core accelerates as the magnetic circuit becomes more efficient, increasing the coil’s inductance, and thus the impedance, dramatically. The increased impedance resulting from this initial inrush decreases the current. This gives the power needed to counter enough pressure to open the valve, and then actually reduce power demand once a steady state is reached, following the curve depicted in Figure 2.
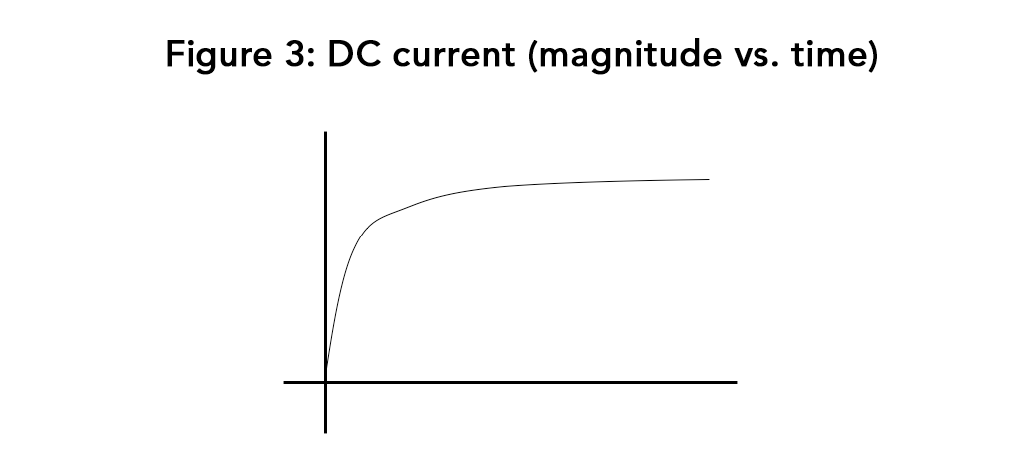
With DC excitation, however, the case is reversed. Applying DC voltage to a solenoid coil actually increases the current asymptotically (Figure 3) until it is equal to voltage divided by the coil resistance. The time it takes to get to that steady-state level depends on the time constant of coil inductance divided by resistance (L divided by R). Thus DC excitation, with its relatively slow buildup of current, creates exactly the opposite of the quick spike necessary for energy efficient operation.
Although AC excitation is typically more efficient, it is not necessarily the best choice. AC usually
comes with high voltages (120/240 V AC), which raises user issues such as wire segregation and
shock hazards. Low-voltage AC is of course available, but requires a transformer, which introduces
power/heat issues.
AC excitation is also subject to intrinsic losses. Since the voltage/current is cycling, in an AC solenoid
substantial “iron losses” (hysteresis and eddy currents) can account for half of its power dissipation.
AC is also not as suitable to many modern industrial applications that use programmable logic
controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCSs), and other digital technologies that automate
fluid control and provide easier connectivity to DC loads. DC power leverages its capability to offer
more outputs per plug-in module or enable the user to share one output module between different load
types. And DC power busses are often more readily available (e.g., 24 V DC with auctioneered backups
in many process plants).
The ideal solution would be to achieve the current waveform “shape” of AC solenoid excitation without
all the inherent limitations. To accomplish this, some solenoid valve packages deploy additional electronic
components to bring the shape of the DC coil current waveform closer to AC curve. Figure 4 depicts a
simple example of the operation of these additional “spike and hold” circuits.
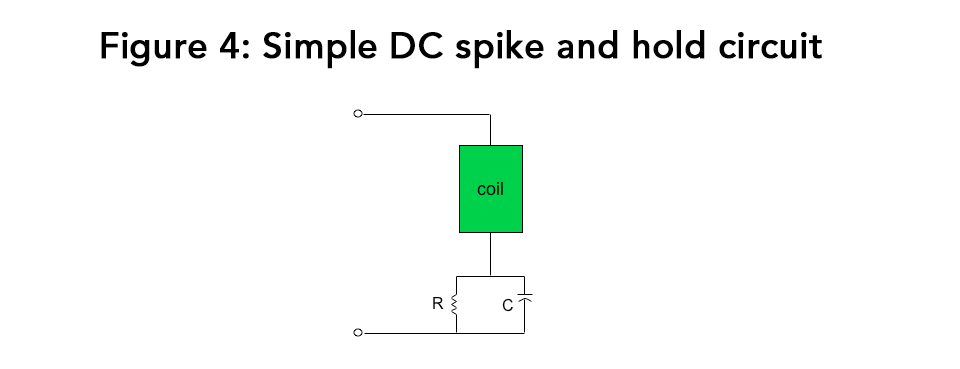
When the coil is first energized with direct current, it spikes through and charges a capacitor (C).
It then encounters the added resistor (R), which limits its continued flow through the coil, thereby
minimizing subsequent energy consumption. But using an additional resistor, or any similar heat generating component, in this way also adds heat to the system, confining this approach to smaller-sized solenoid valves.
Yet it is the larger solenoids in which power conservation has the greatest payback. What’s needed
is a way to generate a high-current initial pulse from a DC voltage rail, and then reduce it quickly to the
minimum power level needed to keep the solenoid valve open, and do so without dropping the steady state current through a resistor, linear-mode transistor, or other technology that consumes more power
than it saves.
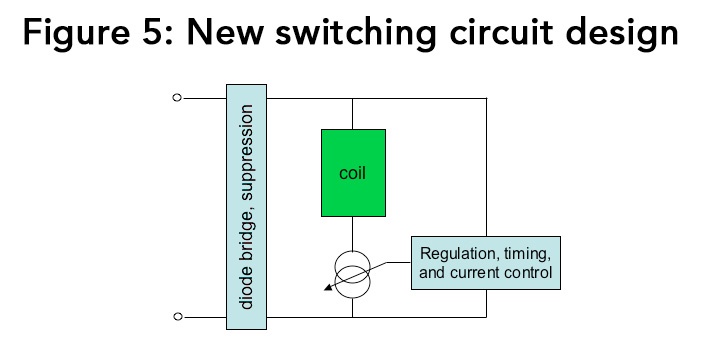
ASCO Valve has accomplished this through the development of an integral switching power supply
that accepts a wide range of both AC or DC input. Its circuits can be programmed to supply increased
current to the coil during initial excitation and then drop back to maintenance current.
Embodied in ASCO’s RedHat Next Generation™ valve line, this technology delivers much improved
fluid performance, with higher flow rates and pressures, at a fraction of the steady-state electrical power
consumption of conventional designs. It also minimizes problems related to heat buildup in
solenoid operation.
Along with the high operating costs associated with excess power production are the performance and
maintenance complications from the heat itself. A bank of ten conventional 11-watt solenoids in a sealed
cabinet, for example, can quickly raise internal temperatures beyond the specifications of other electronics
in the cabinet. Removing that heat from instrumentation systems can require fans, air-conditioning, or other
cooling apparatus.
That solenoid coil heat also reduces a valve’s life expectancy. Differing grades of magnet-wire/insulation
do allow for larger or smaller tolerances for ambient system temperatures and for the increased temperature
caused by a valve’s own heat of operation, but eliminating the production of unnecessary heat in the first
place makes more sense from both an operational and an economic perspective.
There is even a “ten degree C” rule of thumb, which suggests that a coil’s thermal life approximately
doubles for every ten degree Celsius reduction in operating temperature, all other things being equal.
This is based on Arrhenius’ theory applied to a typical activation energy. If the current switching system
mentioned above can reduce the output of conventional 11-watt solenoid coil by 2 watts, it would reduce
coil temperature by about 40 degrees C, resulting in a lifetime increase of 2^(40/10), or 16, meaning that
you could extend the service life of a solenoid coil from 5 years to 80 years.
Eliminating unnecessary power consumption in solenoid coils saves money, improves valve performance,
and extends valve operating life. New digital designs overcome the energy consumption limitations of
conventional AC and DC powered systems with a switching power supply that enables users to deploy
either AC or DC current for their applications, in a way that provides the initial power spike necessary to
open the valve, while reducing power demand to low levels needed to maintain steady state operations.
The benefits are lower energy costs, lower failure rates, reduced maintenance costs, and dramatic life
extension of the valves.
Copyright © 2025 Butler & Land Technologies, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Web Design by Red Spot Design. Return & Refund Policy, Terms & Conditions